As our parents and grandparents age, many of us cannot help but think of what conditions may affect them. Among those that prompt the greatest amount of concern is vascular dementia.
Being fearful of a condition that affects the mind is understandable, but we cannot afford to be overwhelmed by that sense of dread. To tackle it capably and give our loved ones the support they need, we must better recognize what we are dealing with.
This article will focus on all facets of vascular dementia. Please read on to find out more about how it affects the human mind. We’ll also talk about how to recognize that condition as well as the steps we can take to prevent it.
What Is Vascular Dementia?
To start, let’s first talk about what vascular dementia is.
Vascular dementia affects a person’s ability to think. According to the Mayo Clinic, it impacts a person’s ability to make plans, develop reasoning, and render judgment. It can even affect a person’s memory.
The reason why the brain’s capacity deteriorates in that manner is due to brain damage. That damage is the result of the brain receiving inadequate blood flow. There are several potential explanations for why the blood flow to the brain gets disrupted, and we’ll get into those later in the article.
For now, let’s first address a question about vascular dementia that’s likely on your mind.
How Do Dementia, Vascular Dementia, and Alzheimer’s Disease Differ from One Another?
It’s important to note that dementia and vascular dementia are not the same things. Vascular dementia is a more specific form of dementia, often distinguishable by how people develop it.
Vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease are easier to compare. While professionals can trace the onset of vascular dementia back to poor blood flow to or within the brain, the main causes of Alzheimer’s Disease are tougher to pin down.
There’s also a big difference between how common the conditions are. According to VeryWell Health, estimates suggest that around 10 percent of all people with dementia in the United States are affected by the vascular kind. The numbers are clearer when it comes to Alzheimer’s Disease because an estimated 5 million Americans are currently dealing with the condition.
Risk factors are quite similar between vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease. Chronic ailments that affect the heart and blood are major risk factors for vascular dementia, and the same goes for Alzheimer’s Disease. Age and genetics are also known risk factors for both conditions.
As for the symptoms, there is a significant amount of overlap between the two conditions. The only real difference is that the symptoms of vascular dementia may appear suddenly due to a recent health episode. In people with Alzheimer’s Disease, the emergence of symptoms may take place over a longer time.
What Are the Causes of Vascular Dementia?
The main reason why people suffer a cognitive decline and develop vascular dementia is due to inadequate blood flow to the brain. Similar to other internal organs, the brain needs the oxygen and nutrients found in the blood to function properly. Without proper nourishment, your brain cells will wither away and eventually perish.
There are different possible explanations for why not enough blood is making it to your brain. We’ve highlighted them below.
Stroke
A stroke takes place when the blood supply to the brain is suddenly cut off. There are three types of strokes people may experience.
The first is known as an ischemic stroke, and it happens whenever blood flow within an artery leading to the brain is interrupted by a clot or some other form of blockage. Ischemic strokes account for 80 percent of all strokes, according to The Internet Stroke Center.
A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when an artery leading to the brain suddenly ruptures. If the rupture leads to blood releasing into the brain, professionals regard the incident as intracerebral hemorrhage.
Vascular dementia can be a side effect of all three types of strokes.
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis takes place over a long period of time. If you have this condition, your arteries will continue to get narrower due to plaque buildup. The condition can progress to the point where your blood will have a harder time passing through your arteries.
The longer that condition remains unaddressed, the harder it will be for your brain to receive the nutrients it needs. Both your body and your mind will suffer the ill effects of atherosclerosis, and eventually, vascular dementia.
Accidents
An accident can cause all kinds of damage to your body. Even the arteries leading to your brain are susceptible.
If those arteries get damaged because of an accident, you may suffer from a hemorrhage and the different complications they can cause. Among those complications is vascular dementia.
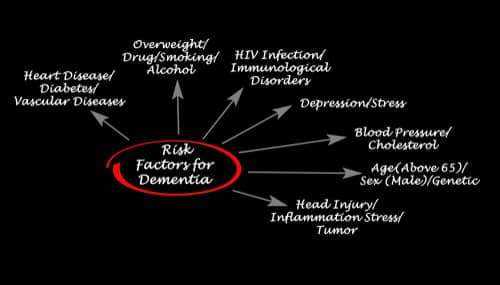
What Are the Risk Factors for Vascular Dementia?
How at risk you are for vascular dementia depends on a wide variety of factors. These include factors you can control and those you cannot.
High Blood Pressure
Having high blood pressure takes a great toll on your body. In this case, the cause of concern is related to how much stress your blood vessels, such as your arteries, will have to endure.
The continuously high blood pressure can gradually wear down your arteries to the point where they are no longer functioning as intended. Once the arteries leading to your brain get worn down, you become more susceptible to vascular dementia.
High Cholesterol Levels
We talked earlier about how atherosclerosis is among the main causes of vascular dementia. We also touched on the fact that atherosclerosis is often because of plaque buildup along your arteries.
Among those substances that may accumulate inside your arteries is cholesterol. To be more specific, the so-called “bad” cholesterol, otherwise known as low-density lipoprotein, is what puts you at risk for vascular dementia.
Diabetes
Individuals who have diabetes have high glucose levels. That’s problematic because the glucose can be damaging, especially to your different blood vessels. As your blood vessels continue to sustain damage from the glucose, the odds of you developing vascular dementia increase.
Smoking
Many people know that smoking is bad for the lungs, but what many fail to understand is that it can be damaging beyond that. Other parts of your body are also adversely affected by your smoking habit, including your blood vessels.
The damage that a smoking habit can inflict upon your blood vessels can be severe, and it could be why you start to suffer from vascular dementia.
Lack of Exercise
You need to keep your arteries healthy if you want to give yourself the best chance of avoiding vascular dementia. Exercise helps with that.
According to this article from Harvard Health, exercising more boosts the nitric oxide production of your endothelial cells, which is a good thing. That nitric oxide plays an essential role inside your body as it maintains the slipperiness of the arteries while also relaxing their smooth muscle cells.
Nitric oxide helps promote better blood flow throughout your body by accomplishing those two things. Your brain will receive a steady supply of the nutrients it needs, thanks to that.
Aging
One of the inescapable truths of life is that the body weakens as it ages. You cannot reverse that. Even your arteries will weaken due to the wear and tear brought about by aging, and that can potentially lead to vascular dementia.
Atrial Fibrillation
Unlike the other risk factors mentioned in this section, atrial fibrillation is something you can potentially prevent or something out of your control. Atrial fibrillation is otherwise known as an irregular heart rate that tends to be on the faster side.
The abnormal rhythm of your heart can spell trouble because it can lead to the formation of blood clots.
It’s possible for atrial fibrillation to be caused by high blood pressure, lung disease, or even a mistake made during an earlier surgical procedure you had. However, your genetics can also play a role here as abnormal heart valves and congenital heart defects are known causes of atrial fibrillation.
What Are the Symptoms of Vascular Dementia?
Many of the symptoms linked to vascular dementia affect the mind. The people who have this condition may have a difficult time analyzing situations, concentrating, and making plans. Someone with vascular dementia may also become unable to come up with a decision in a timely manner.
It’s not only a person’s ability to think critically that is impacted by vascular dementia. Their mood may also become more unstable because of their condition. They may become more prone to agitation and/or experience bouts of depression more often.
Recalling memories is yet another frequent source of frustration for people affected by vascular dementia. It is also not unusual for people with this condition to lose interest quickly.
There are also physical manifestations of vascular dementia that are important to look out for. If you have a loved one affected by this condition, monitor how they walk closely because it may become unsteady. Weakness affecting one side of the body is another symptom to keep close tabs on.
How Can You Prevent Vascular Dementia?
Given how difficult it can be to live with the symptoms of vascular dementia, preventing the condition in the first place would be the ideal course of action. There is no secret to preventing vascular dementia. The best way to avoid it is to lead a healthy lifestyle.
Start with your diet.
Evaluate what you eat regularly and see if your favorite foods may lead to a diagnosis of high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or diabetes. If that is the case, then it’s time for you to eliminate or at least minimize your consumption of those foods.
Replace them with more nourishing foods such as whole grains, vegetables, lean proteins, and berries. Every now and then, enjoying a bite of dark chocolate is acceptable as it can contribute to improved blood flow.
As always, remember to eat in moderation.
This is also a good time for you to adopt an exercise plan. Give your body a fighting chance against dementia by training it regularly.
You don’t need to take on a rigorous training program. Anything that gets you moving regularly for a good chunk of the day will be beneficial. Going on runs or walks around your neighborhood still counts as exercise.
Needless to say, you should also drop your smoking habit if you haven’t already. Nothing good can come from a smoking habit, and your body will thank you for dropping it.
How Is Vascular Dementia Treated?
Currently, there is no known cure for vascular dementia. Does that mean that you cannot help your loved ones who already have this condition? That is not the case.
The key here is to address the symptoms.
According to the University of California, San Francisco, forms of medication to treat memory problems, depression, and anxiety can also be given to patients with vascular dementia. Those medications can help with managing the symptoms.
Exercising also remains beneficial even to those who have already have vascular dementia. Regular exercise should help slow down the deterioration of the arteries and potentially prevent the presenting symptoms from getting worse.
You can also enlist the help of assisted living facilities to take better care of your loved one who has vascular dementia. Along with keeping a watchful eye on your older loved ones, the facilities will also ensure that they take their medication on time and encourage them to participate in various activities.
Vascular dementia must be taken seriously. Failing to do so can severely affect the quality of life that your loved one enjoys.
We at Lakeside Manor will help all our residents maintain a good quality of life regardless of the conditions they are dealing with. Contact us today to learn more about how we can assist you and your family members.